Takayasu Arteritis Treatment and Its Medicine List
Arteritis means an inflammation of the arteries. Takayasu's arteritis is a chronic, auto-immune disease in which your body's defense system accidentally attacks your arterial walls and destroys them. This disease may be reversible initially but eventually progresses to irreversible changes in the arteries... Large arteries like the aorta and its main branches are commonly involved in TAK.
What causes TAK?
The exact cause of Takayasu's arteritis is not known. There are genetic and immunological factors and certain infections considered responsible for causing Takayasu’s arteritis.
How many people suffer from this disease?
- Takayasu’s arteritis is a rare disorder with more cases seen in India, Japan, Asia, and Mexico.
- Approximately 1.2 to 2.6 cases per million person-years.
- It is more often seen in women under the age of 40 years.
Symptoms
Symptoms may range from asymptomatic/silent to serious manifestations like
impalpable pulse or bruits (Audible murmurs-a type of sound or palpable thrills over large arteries).
Few non-specific symptoms of the disease:
- Sense of generalized illness (malaise), low-grade fever, swollen glands, anemia, dizziness, night sweats, muscle aches or arthritis, weight loss, lack of blood supply to vital organs.
- Claudication (pain in legs or arms that occurs while working or walking)
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon (decreased blood flow to the fingers)
- Visual changes
- Passing out or fainting
- Temporary stroke-like symptoms disappear and come again on their own
- Stroke
- Abdominal pain, Nausea, Vomiting
- High blood pressure
- Kidney failure
- Aortic insufficiency (heart valve disease where the aortic valve functions inadequately)
- Heart failure or heart attack
Which arteries are commonly affected?
Subclavian artery (93%), Common carotid artery (58%), Abdominal aorta (47%), Renal artery (38%), Aortic Arch (35%), Vertebral arteries (35%), Coeliac axis (18%), Superior mesenteric (18%), Iliac arteries (17%), Pulmonary arteries (10-40%), Coronary artery (<10%).
Diagnosis
It is often difficult to diagnose Takayasu’s disease. Doctors generally find it on Angiogram/ angiography.
Some of the criteria for diagnosis are:
Important and compulsory criteria1:
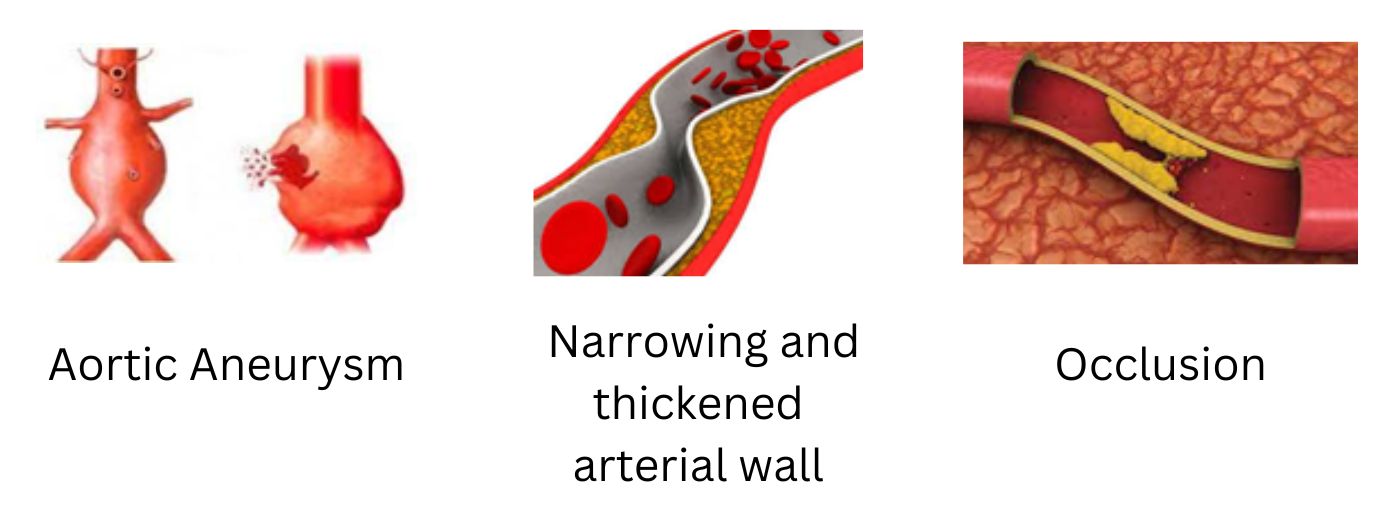
Angiography must show the presence of dilatation, narrowing, or complete blockage or thickening of the arterial wall and is generally not due to any other existing pathologies in the aorta or its branches or pulmonary arteries.
One of these five criteria:
- Absent or decreased or asymmetrical peripheral artery pulse
- Bruits - Audible murmurs(a type of sound) or palpable thrills over large arteries
- Difference of four-limb systolic blood pressure - more than 10mm Hg in any limb
- High level of C reactive protein CRP and ESR >20mm/hr.
Similar conditions
Takayasu arteritis may resemble the following chronic diseases.
Giant cell arteritis, Neurofibromatosis, Kawasaki disease, Polyarthritis nodosa, Wegener's granulomatosis disease, Rheumatic Fever, Sarcoidosis, SLE, Bechet’s disease, Spondyloarthropathies, Inherited connective disorders, Congenital aortic abnormalities, Fibromuscular dysplasia,
Investigations:
Currently, there is a lack of a gold standard for the monitoring of progress or the disease activity of Takayasu arteritis.
Few of the tests that can help are :
CRP, PET-CT,ESR, contrast MRI , CT angiography, Formal digital subtraction arteriography.
Classification2
Type 1: Aortic arch and its branches
Type 2a: Aorta ascending branches and aortic arch
Type 2b: Type 2a+ thoracic descending aorta
Type 3: Involves thoracic descending aorta abdominal aorta and renal arteries
Type 4: Includes involvement of aorta in the abdominal region and or renal arteries
Type 5: Involvement of complete aorta and renal arteries
Complications:
Acute inflammation can destroy the arterial wall leading to an aneurysm (Balloon bulge formation due to the weak artery wall) and its rupture.
Chronic vessel wall inflammation (swelling) leads to thickening, fibrosis, stenosis (narrowing), and thrombus formation (clot formation) evolving into congestive Heart failure (heart failure), Cerebrovascular accident (stroke), Myocardial Infarction (Heart attack), kidney failure.
Conventional Medicine Treatment:
Glucocorticoids and Methotrexate are helpful treatments for alleviating symptoms. An aggressive surgical approach to prevent complications can decrease the mortality rate.
Homeopathic treatment :
Written & Approved by-
Dr. Rajesh Shah
M.D. (Hom.)