Symptoms for Eczema in Kids and Adults
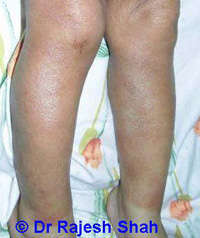
Atopic dermatitis presents with inflamed skin. The typical rash or eruptions are dry, scaly, red, and itching. The skin eruptions could affect any part of the body, however, it is more common on the face, folds of hands, and feet. The predominant symptom of Atopic dermatitis is intense itching. A thin watery discharge may ooze after itching. There may also be minor bleeding on scratching. Some of the lesions might get infected by contamination with bacteria, leading to pus formation.
Most of the patients which are treated conventionally with the use of cortisone in the form of topical cream or oral tablets; have a tendency to
get suppressed. The patient and parents might get a sign of relief, least realizing that the effect of cortisone is only superficially and the disease will come back with vengeance.
It is a common phenomenon that patients tend to keep on using cortisone, masking the disease, and the disease goes deeper and deeper.
Dermatological distribution of the skin lesions as per age
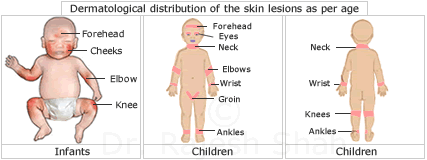
Symptoms in Infants:
In infants, symmetric lesions are found over the face (cheeks, forehead, scalp, and trunk), on the outer surface (extensor) of the extremities, scalp (sometimes causing alopecia). In extensive cases, the rash can be found even on the flexor surfaces of the extremities.
Symptoms in Children:
There is a presence of symmetric lesions on the wrist, ankles and the flexor areas of the limbs. Generalized lesions spread all over the body can also be found in this age group.
Eczema Symptoms in Adults:
Predominantly affects the flexor areas of the arms, legs, and neck. Other areas which can be affected are the groin, axillary, etc.
Stages of Atopic dermatitis:
The skin lesions of Atopic dermatitis vary according to the stage of the disease.
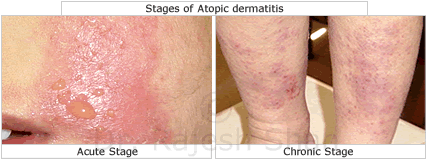
Acute stage:
On examination, the lesions appear wet due to serous (thin) exudates from the erosion. Papules (flat bumps) and vesicles (fluid-filled eruptions) are present on reddish skin.
Sub-acute:
The characteristic features of the skin at this stage of the disease are - scaling of the skin, and excoriated and fused papules over erythematous (red) skin.
Chronic Stage:
In chronic cases, the skin is typically thickened and has pigmentary changes (hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation). The papules are excoriated and there is a presence of nodules on the skin. Intense itching is present in all stages of the disease hence the person tends to scratch all the time, which often leads to secondary infection of the lesion. As a result, the lesion develops yellow crust over-laying pus and is surrounded by erythema.
Related manifestations are:
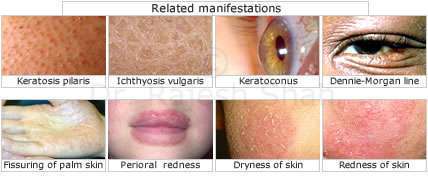
:: Keratosis pilaris: Small and pointed asymptomatic rough bumps on the extensor surfaces of upper arms, buttocks and anterior of thighs.
:: Ichthyosis vulgaris: Presence of polygonal fish-like scales especially on the legs. Hyperlinear (thickened skin with increased visible lines) palms and soles.
:: Keratoconus: A cone-shaped cornea develops in severe cases, mostly in the second or third decade of life.
:: Dennie-Morgan line: Prominent skin folds below the eyes
:: Fissuring of the skin of palms, soles, and fingers often occurs.
:: Redness of the face
:: Perioral (around the mouth) pallor
:: Dryness of skin
:: Asymptomatic hypopigmented areas on face and shoulders
Written & Approved by-
Dr. Rajesh Shah
M.D. (Hom.)